Peripheral blood cell-specific cytokines in persons with untreated HIV infection in Malawi, Africa
Abstract
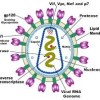
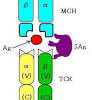
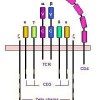
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is the primary cause of morbidity and mortality in Malawi, Africa, because of its many effects on the immune system. Immune cells communicate through cytokines; therefore, we examined the relationships between HIV serostatus and cell-specific cytokine production for 40 asymptomatic, employed adults and 312 acutely ill, hospitalized patients in Malawi.… Read more