Vitamin A levels and immunity in humans
Abstract
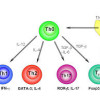
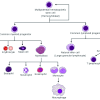
In animal studies, vitamin A deficiency induces a shift from type 2 (humoral, Th2) to type 1 (cellular, Th1) cytokines; there are no similar data for humans. Control of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections requires type 1 cytokine (cellular) immunity.… Read more